Neo4j > Data Model > Data Layout
Neo4j is based on the property graph model which is similar to an entity relationship diagram. The property graph model is composed of a set of nodes that are connected by relationships. As seen below, the nodes acts as entities that have one or more attributes stored as properties. They can be tagged with one or more labels to distinguish them from other nodes and speed up queries. Relationships can have properties as well and can be tagged with only one relationship type. Relationships must have a start and end node and will be deleted if one of the attached nodes are removed.

As seen from the property graph model of Neo4j, we need to understand our data model and transform it into nodes with labels having relationships between them. Once we designed our data model in the graph model, we can answer our queries easily using the Cypher language.
The first step to design your data model according to the graph model is to describe how exactly your data is related to each other. For example, if you want to transform your B2C data model to the graph model, you would think of a simple statements to describe your model. Let's assume we have only three entities: customers, orders, and products. Then a simple description of the model will be:
"We have some customers who can create some orders and each order can contain some products"
In order to design the graph model out of the above statement, first we need to extract the nodes and tag them with appropriate labels.

As seen from the statement above, we can extract three entities: customer, order, and product. They can be easily tagged with ":Customer", ":Order", and ":Product" labels.
After extracting the nodes and their labels, we should now extract the relationships between them if any. As can be seen from the statement describing the data, we have three different relationships. Each customer creates an order, the relationship can have a type called OWNS_AN or any similar name. Then the order contains one or more products, so the relationship can be of type CONTAINS. So we can extract two relationship types OWNS_AN and CONTAINS.
After defining the node labels and the relationship types, we can easily build the graph model. For instance let's assume we have a simple data as described by the below two statements:
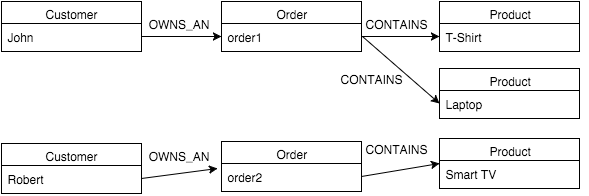
"A customer called John has created an order containing two products (T-Shirt and a laptop)" "A customer called Robert has created an order containing one product (Smart TV)"
From the data above, we know that we need to create two nodes with label :Customer, two nodes with label :Order and three nodes with label :Product.

After creating the nodes and tag them with their corresponding labels, we need to create the relationships between them. From the statements above, we need to create one relationship between john node and order1 with type OWNS_AN, one relationship between Robert node and order2 with type OWNS_AN, two relationships between order1 node and the T-Shirt and Laptop nodes with type CONTAINS and finally a relationship between order2 and the Smart-TV node with type CONTAINS as shown below:
Now after we have successfully created the graph model, we can easily use Cypher language to run simple or complex queries.
To migrate your data model from relational to graph model, you need first to create the labels which corresponds to the table names. Then each row in the relational data model will correspond to a node in the graph model that is tagged with a label corresponds to the table name. Then the columns in the relational tables can be stored as properties for each node ignoring any columns having null values. Table primary keys can be enforced using a unique constraints. Finally table foreign keys will be replaced by relationships representing what the relationship means to other tables and the end node will be the node corresponding to the row in the other table.